Content Studio and content forms
Contents
Introduction to Content Studio, content types and x-data.
Content Studio
Content Studio is the editorial interface used to create and manage content. It was pre-installed from Enonic Market as a part of the Essentials template when you started the sandbox and can now be accessed from the XP menu.
Click Content Studio in the XP menu to launch it.
When your own application was started, it automatically created a content project called Intro Project and populated it with content. Since this is the only available project at the moment, Content Studio will automatically open it, revealing the list of sample content.
| The current project is shown at the top of Content Studio. |
Content type: Person
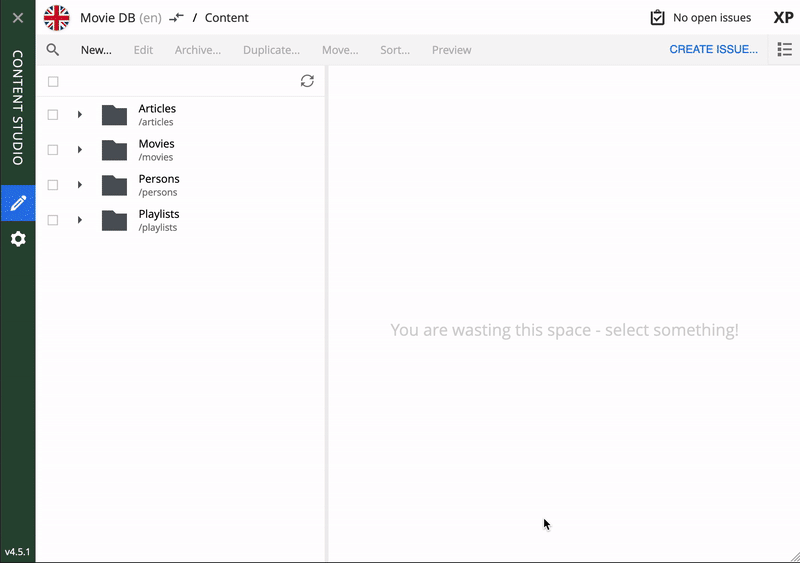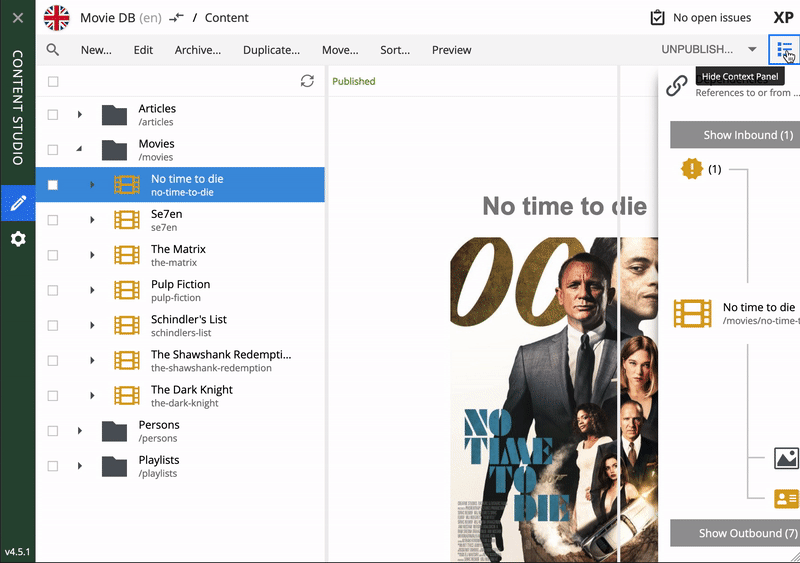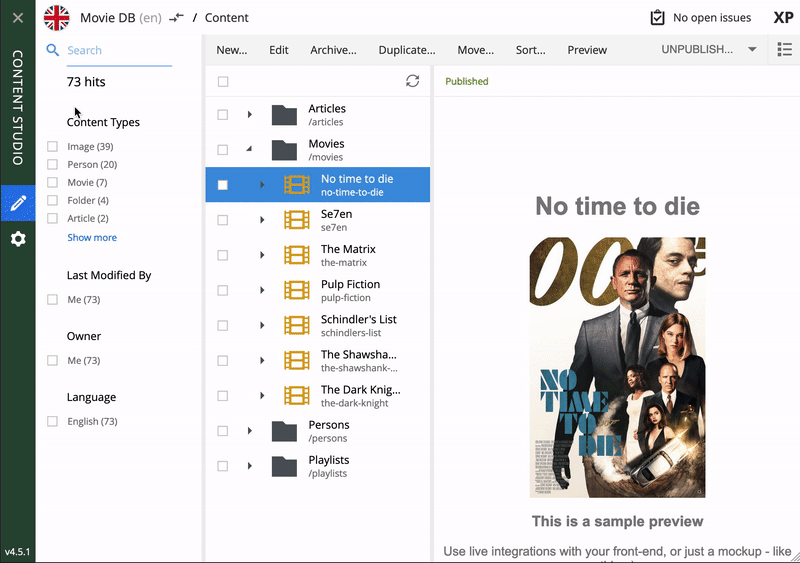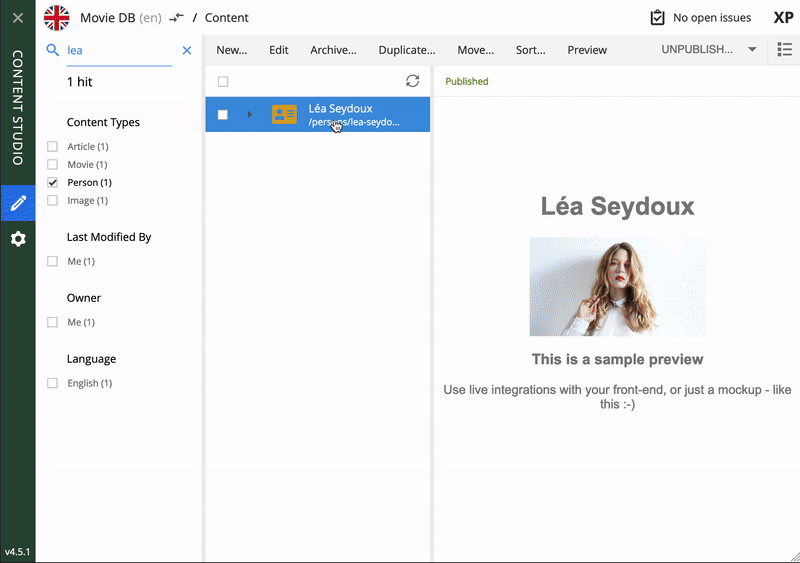
To edit an item, simply select it and click Edit in the menu bar, or by using right click. When editing a Person content item, this is what the form looks like in Content Studio. On bigger screens, you will also get a preview on the right-hand side.
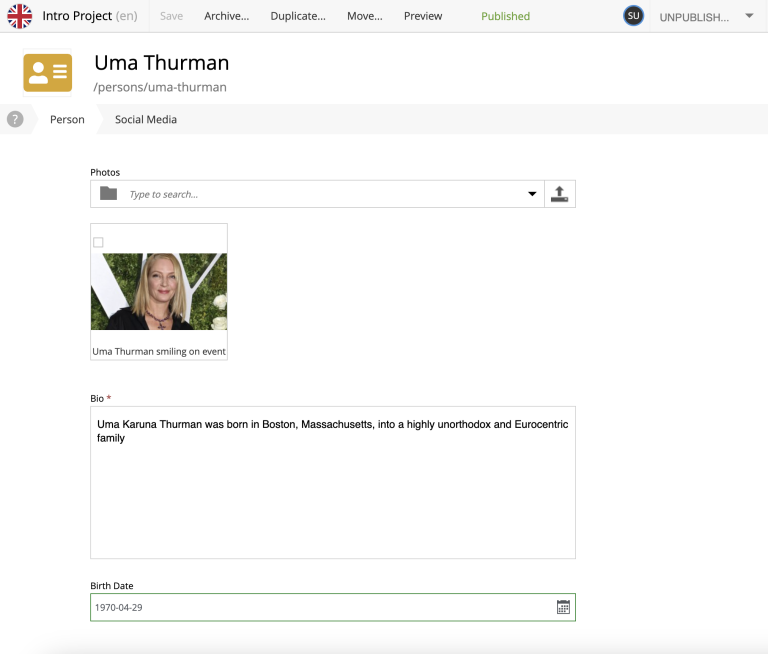
The form comes from the content type definition, which is located inside the app. Here is what it looks like:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<content-type xmlns="urn:enonic:xp:model:1.0">
<display-name>Person</display-name>
<description>Historical or living human</description>
<super-type>base:structured</super-type>
<form>
<input type="ImageSelector" name="photos">
<label>Photos</label>
<occurrences minimum="0" maximum="0"/>
</input>
<input type="HtmlArea" name="bio">
<label>Bio</label>
<occurrences minimum="1" maximum="1"/>
<config>
<exclude>NumberedList Outdent Indent SpecialChar Anchor Table PasteModeSwitcher</exclude>
</config>
</input>
<input type="Date" name="dateofbirth">
<label>Birth Date</label>
<occurrences minimum="0" maximum="1"/>
</input>
</form>
</content-type>When used to create content, it is stored like this:
{
"valid": true,
"displayName": "Uma Thurman",
"type": "com.example.myapp:person",
"owner": "user:system:su",
"language": "en",
"modifiedTime": "2018-07-03T05:58:55.025Z",
"modifier": "user:system:su",
"creator": "user:system:su",
"createdTime": "2018-07-03T05:57:35.292Z",
"publish": {
"first": "2024-01-18T12:08:23.167Z",
"from": "2024-01-18T12:08:23.167Z"
},
"data": {
"photos": "8d47792f-0ae6-4d74-a6e4-bab0e8d2374b",
"bio": "Uma Karuna Thurman was born in Boston, Massachusetts, into a highly unorthodox and Eurocentric family",
"dateofbirth": "1970-04-29"
}
}X-Data: Social media
When editing a Person, you’ll notice an additional subset of fields inside the Content form with the title Social Media. This is, strictly speaking, a separate form, injected into the Person content type - we call it "eXtended data" (or just "x-data").
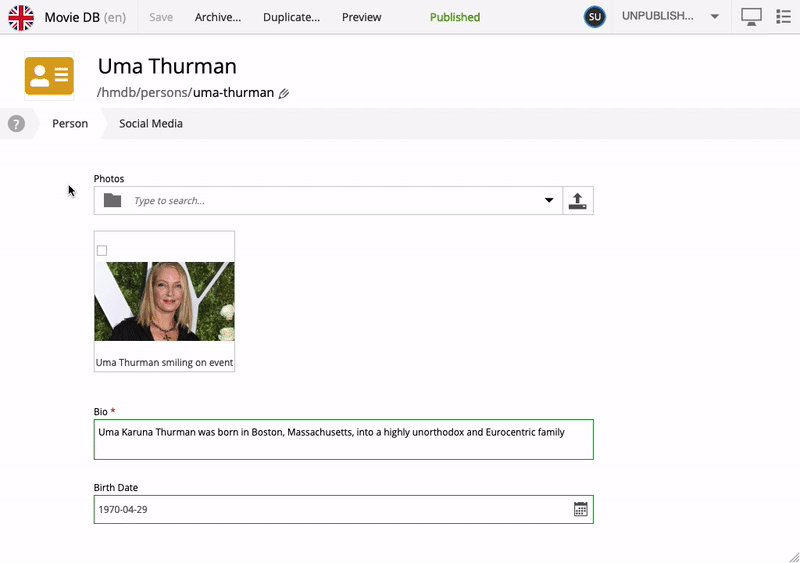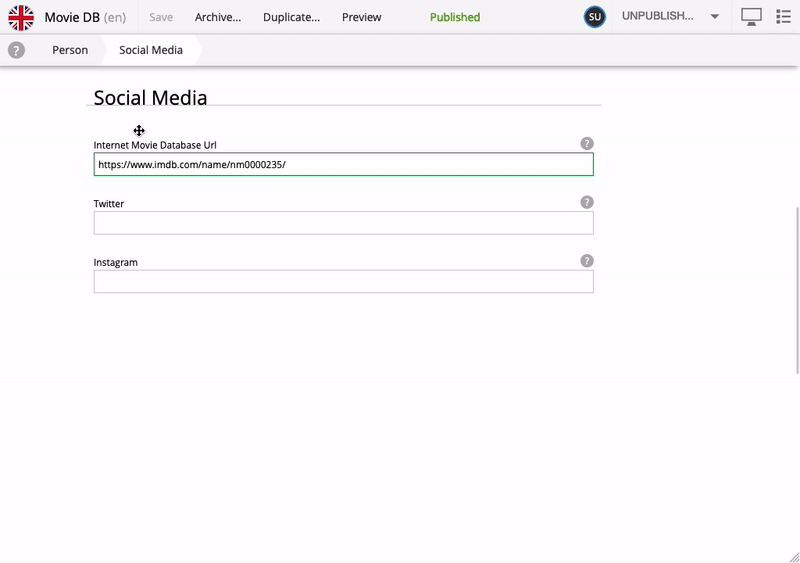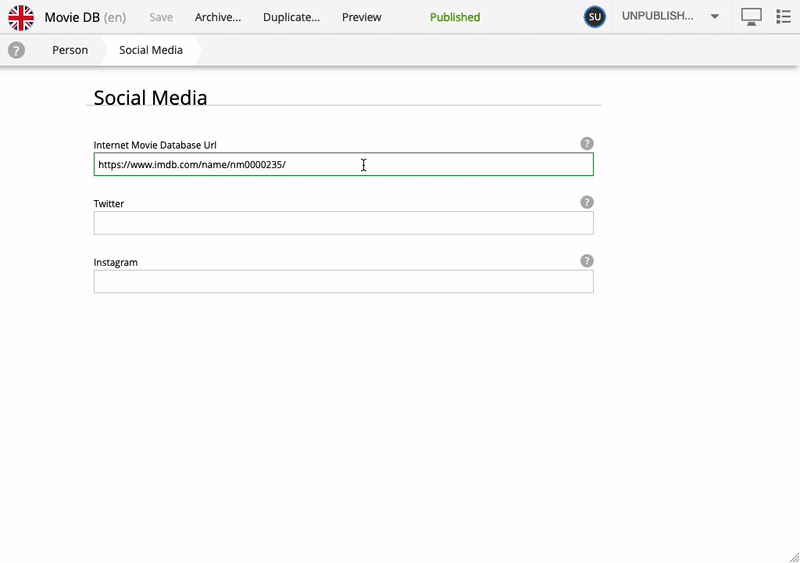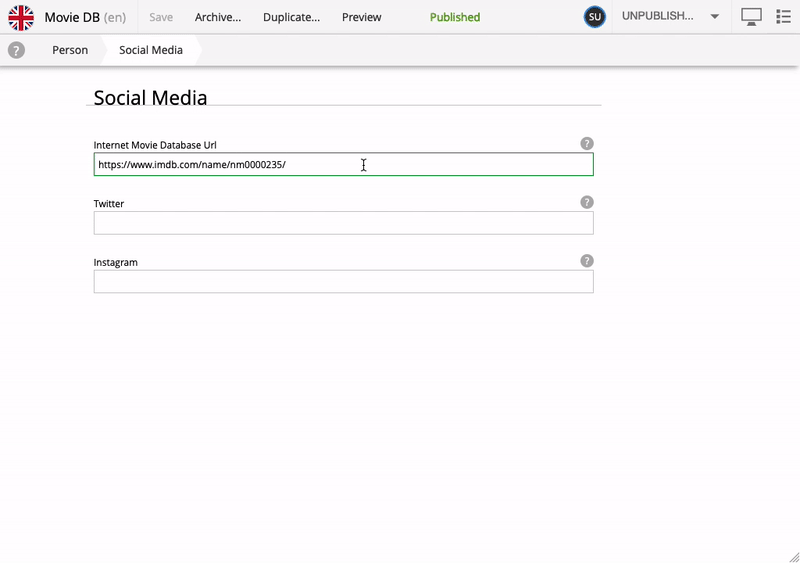
X-data can be applied across multiple content types. In this app for instance, the Social Media form is also available on the Movie content type. More interestingly, X-data can even be injected from a different application - at runtime.
This is what the definition looks like:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<x-data>
<display-name>Social Media</display-name>
<form>
<input type="TextLine" name="imdb">
<help-text>URL to IMDB</help-text>
<label>Internet Movie Database Url</label>
<occurrences minimum="0" maximum="1"/>
</input>
<input type="TextLine" name="twitter">
<help-text>Twitter Handle - i.e. @enonicHQ</help-text>
<label>Twitter</label>
<occurrences minimum="0" maximum="1"/>
<config>
<regexp>^@?(\w){1,15}$</regexp>
</config>
</input>
<input type="TextLine" name="instagram">
<help-text>Instagram Handle - i.e. @username</help-text>
<label>Instagram</label>
<occurrences minimum="0" maximum="1"/>
<config>
<regexp>^@?(\w){1,28}$</regexp>
</config>
</input>
</form>
</x-data>You can also see what the persisted version looks like in the JSON.
{
"data": {
"photos": "8d47792f-0ae6-4d74-a6e4-bab0e8d2374b",
"bio": "Uma Karuna Thurman was born in Boston, Massachusetts, into a highly unorthodox and Eurocentric family",
"dateofbirth": "1970-04-29"
},
"x": {
"com-example-myapp": {
"SoMe": {
"imdb": "https://www.imdb.com/name/nm0000235/"
}
}
}
}Adding a new content type
Let’s do a practical exercise by adding a new content type called Review to your app. This will allow you to create reviews of movies.
-
From inside the
samples/folder of your app, copy or move thereview/folder tosrc/main/resources/site/content-types/. -
Write a review. Content Studio should pick up the changes immediately. From the Content navigation view click New, then select content type
Reviewand start filling out the form fields in the new content item.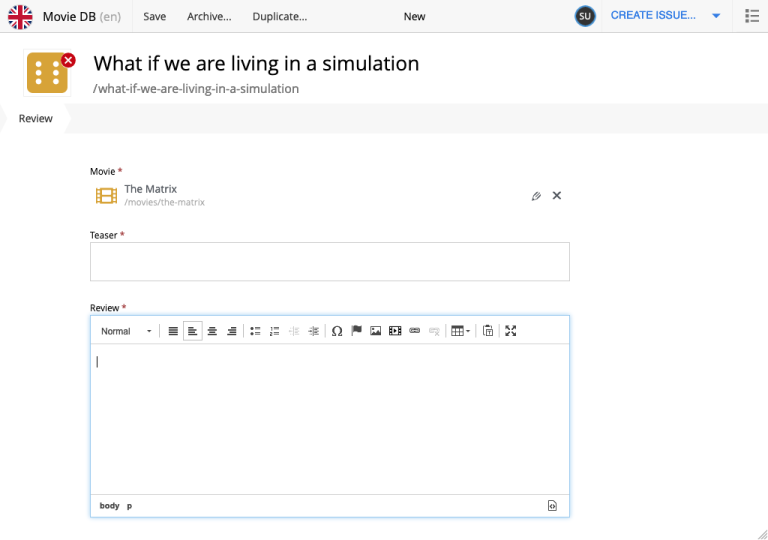
Next up
You’re now familiar with the XP Admin, Content Studio, Content type, and x-data schemas. In the following chapter, you’ll get to play with Query Playground, and the Headless Content API, aka Guillotine.