Common components and props
Contents
In this chapter you’ll add global styling and a footer component to the site
Global CSS
By adding a global CSS file, we avoid repeating common styling for every component.
Follow the steps below:
-
Create a CSS file in the component directory:
react4xp/components/globalStyles.csshtml { background-color: #0b1d30; color: ghostwhite; font-family: "Helvetica Neue", Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; padding: 0; } body { margin: 0 auto 0 auto; } #PageView { width: 100%; } .contentContainer > div { margin-bottom: calc(6vh - 16px); min-height: 86vh; padding: 8px; max-width: 1400px; padding-inline: 2.5vw; margin-inline: auto; } h1 { color: #0892D4; font-size: 3rem; margin: 0 0 3rem 0; padding-top: 3rem; text-align: left; line-height: normal; } h2 { color: #EF82F0; font-size: 2rem; } h3 { color: #61DBFB; font-size: 1.4rem; } a { color: #61DBFB; } img { object-fit: cover; object-position: 50% 50%; max-width: 1600px; } p { font-size: 22px; } .editor-align-justify { margin-inline: auto; } .contentContainer > div > .helloPage { margin-bottom: unset; min-height: unset; padding: unset; } .helloPage { min-height: calc(92vh - 7rem); h1 { color: #61DBFB; } button { background-color: #61DBFB; color: #0b1d30; border: 2px solid #61DBFB !important; box-shadow: 0 0 4px #61DBFB; height: fit-content; } button:hover { box-shadow: 0 0 16px #61DBFB !important; } button:active { background-color: #EF82F0 !important; box-shadow: 0 0 8px #EF82F0 !important; border-color: #EF82F0 !important; } } -
Register the file in App.tsx by adding the following line
react4xp/entries/App.tsximport '../components/globalStyles.css';
Refresh the Hello page to see the what happened:
Footer component
App.tsx is the common starting point for all rendering, and can be used for more than simply styling, for instance by adding a footer.
Follow the steps below to get a glorious new footer across all pages in the site.
-
Add the footer component:
react4xp/components/common/Footer.tsximport React from 'react'; import styles from './Footer.module.css'; export interface FooterProps { logoUrl: string; } const Footer = ({logoUrl}: FooterProps) => ( <footer className={styles.footer}> <div className={styles.footerContainer}> <p> <span className={styles.rotateRight}>©</span> {` ${new Date().getFullYear()}, Built with `} <a href="https://reactjs.org">React4XP</a> </p> </div> {logoUrl && ( <div className={styles.logoContainer}> <img src={logoUrl} width={32} height={42} alt="Enonic XP logo"/> </div> )} </footer> ); export default Footer; -
Add a dedicated CSS module for the footer.
react4xp/components/common/Footer.module.css.footer { margin: 1vh auto auto auto; width: 100%; text-align: center; background-color: black; position: absolute; left: 0; font-size: 18px; height: 7vh; min-height: 45px; align-content: center; } .footer a { color: #61dbfb; text-decoration: none; font-weight: 500; } .footer a:hover { color: #0892D4; text-decoration: underline; } .footer p { margin: 0 .5rem; } .logoContainer { position: absolute; bottom: 1.5vh; right: 1.5rem; } .logoContainer img { max-width: 2.6vh; min-width: 20px; height: auto; } .rotateRight { display: inline-block; transform: rotate(90deg); } -
Add the Footer component to App.tsx:
react4xp/entries/App.tsximport Footer from "/react4xp/components/common/Footer"; import '../components/globalStyles.css' import {AppProps} from '/types/AppProps'; import type {MetaData} from '@enonic/react-components'; import {BaseComponent} from '@enonic/react-components'; import * as React from 'react'; import {componentRegistry} from '../componentRegistry'; const App: React.FC<AppProps> = ({component, data, common, meta}) => { const compMeta: MetaData = meta as MetaData; compMeta.componentRegistry = componentRegistry; return ( <> <BaseComponent component={component} data={data} common={common} meta={compMeta}/> { (component.type == "page" || component.type == "contentType") && <Footer logoUrl={common.logoUrl as string}/> } </> ); } App.displayName = 'App'; export default App;
We are not entirely done yet, as the Footer component requires some props, in order to work properly (pun intended).
Static asset
To make thigs a bit more interesting, the Footer will render the React4XP logo. This means we will need a URL to a static file.
The logo already exists in resources/assets/react4xp.svg |
The Footer is not part of the ComponentRegistry, but it can still use the dataFetcher to get props. For this case, a data processor can be registered as a common processor. Props from the common processor can be accessed across components.
-
Create a processor:
react4xp/components/common/CommonProcessor.tsimport {assetUrl} from '/lib/enonic/asset'; import type {ComponentProcessor} from '@enonic-types/lib-react4xp/DataFetcher'; export const commonProcessor: ComponentProcessor<'com.enonic.app.hmdb:main'> = (props) => { const logoUrl = assetUrl({path: 'react4xp.svg'}); return { logoUrl }; };It invokes
assetUrl()to get the URL for the logo, and returns it as a prop. -
Register the processor in the data fetcher:
react4xp/dataFetcher.tsimport {DataFetcher} from '/lib/enonic/react4xp'; import {commonProcessor} from '/react4xp/components/common/CommonProcessor'; import {helloProcessor} from './components/hello/HelloProcessor'; export const dataFetcher = new DataFetcher(); dataFetcher.addContentType('portal:site', {processor: helloProcessor}); dataFetcher.addCommon({processor: commonProcessor});Using
addCommonensures this will be executed for every rendering request.Be careful to only get the props you need, or else this may slow down rendering of all pages.
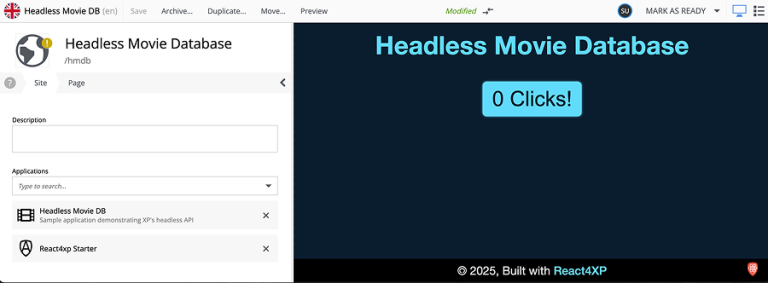
Sweet! You now have a stylish site with a footer component on all pages. The footer also brings it own CSS via a CSS module.
Next
You are on a roll, in the next chapter we’ll be rendering content.