Permissions
Contents
Security of content is determined by the principals and permissions in the content’s security settings. Principals are Users, Groups and Roles which are managed in the Users application. Principals are added to each content. Permissions are granted to the principals of the content.
Principals
Individual users could be added to each content. But security is easier to manage by adding groups and roles to each content and then granting the appropriate permissions to these groups and roles. When a group is added to content then all users who are members of that group will have the group permissions for that content. Similarly, when a role is granted permissions to content, all users who have that role will also have those permissions.
Permissions
Permissions are granted to principals on a per-content basis. This means that changing a principal’s permissions for one content does not affect that principal’s permissions for other content. Below is a list of permissions that can be applied to each principal for any content.
-
Read: The principal can see this content;
-
Create: The principal can create child items under this content. For example, if a user has this permission on a folder then the user can create new content in the folder;
-
Modify: The principal can edit this content and save changes in the draft branch;
-
Delete: The principal can delete this content from the draft branch;
-
Publish: The principal can publish this content to the master branch;
-
Read permissions: The principal can see this content’s permissions;
-
Write permissions: The principal can change this content’s permissions.
Permissions can also be denied to a principal, even if the permissions would otherwise be granted from another principal. For example, all content editors might be added to a group called Content editors which has the Can Publish permissions. But new content editors might break stuff, so they would also be added to a group called Noobs. Users in this group could be prevented from publishing and deleting content by denying those permissions to the group.
Public content
For content to be accessible to the public, (meaning users who are not logged in), it must have the role Everyone with the Read permission. The content must also be published. Content without the Everyone role can only be seen by users who are logged in and have read access to it through one of the content’s principals.
Editing permissions
When a site is first created, it will have the roles Administrator and Content Manager Administrator with full access. It will also have the role of Content Manager App with reading access. When content is created it will inherit the security settings from its parent content. The security settings for any content can be changed through the Edit permissions dialog. This can be accessed with the Edit Permissions button in the Security section when editing content, or by the button in the details panel in browse view.
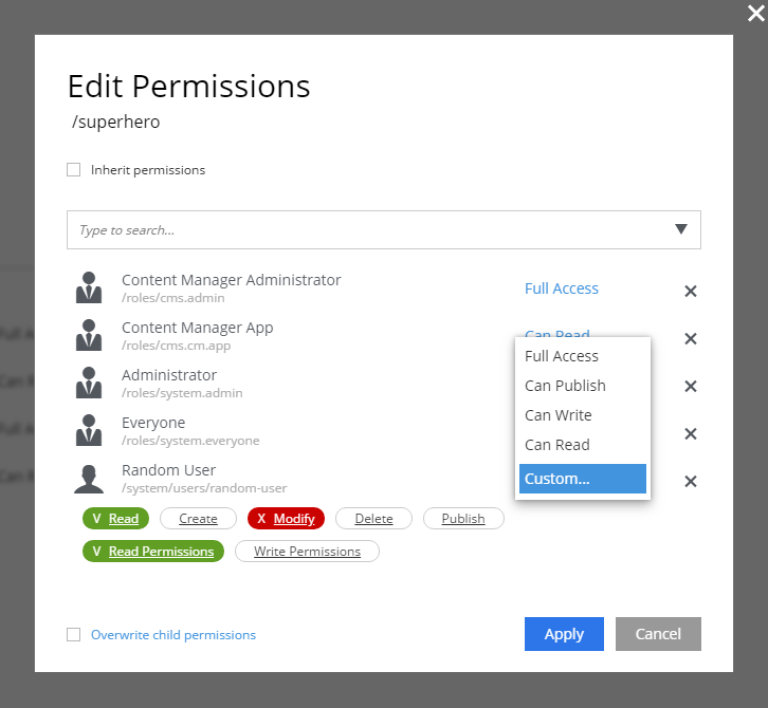
Opening the Edit Permissions dialog shows a list of the current principals and their permissions for the content. By default, all content will inherit permissions from its parent. Permissions cannot be changed until the box for Inherit permissions is unchecked. Any changes that are made will also be applied to all child items that directly or indirectly inherit permissions from this content. There is also a checkbox at the bottom of the dialog labeled Overwrite child permissions. Checking this box will force the new permissions on child content that do not inherit permissions.
When the Inherit permissions checkbox is unchecked, a dropdown selector will appear for adding new principals. The permissions for each principal in the list can be determined by the settings in blue letters on the right. Clicking a setting will open a menu with the available options that can be applied, which are listed below:
-
Can Read: Has only the
Readpermission; -
Can Write: Has permissions for
Read,Create,Modify, andDelete; -
Can Publish: Has permissions for
Read,Create,Modify,Delete, andPublish; -
Full Access: Has all permissions;
-
Custom: Any combination of permissions.
Selecting Custom will list all of the permissions. Clicking on permission will toggle it between white (not granted), green (granted) and red (denied).