Input types
Contents
Input types are the essence of any schema. Their purpose is to enable editing, validation and persistence of data aka content.
Input types have both a front-end and back-end component. The front-end represents the visual editing interface used in the XP admin console, where the back-end is solely used for validation purposes.
An input type produces a single property as output, with zero, 1 or multiple values. This also includes propertySet, which is simply a root node containing multiple properties.
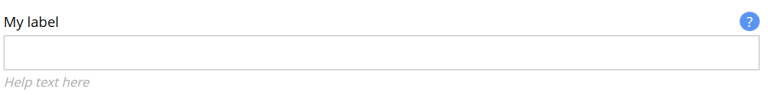
The following configuration is common for all input types:
<input type="InputTypeName" name="myname" > (1)
<label i18n="myname.label">My label</label> (2)
<default/> (3)
<help-text i18n="myname.help-text">Help text here</help-text> (4)
<occurrences minimum="0" maximum="1"/> (5)
<config/> (6)
</input>| 1 | input contains two mandatory attributes:
@name is used when storing the data in a property, and must be unique on each level. @type refers to one of the many input types which are listed below. |
| 2 | label is another mandatory field that holds the human readable value that will be displayed when listing the input type control in the administrative interface
@i18n is an optional attribute holding the key to localization phrase of the form (see localization). |
| 3 | default is an optional field that lets you specify default values to be used by the input type. |
| 4 | help-text is an optional field that lets you specify a text label shown below the input field. Used for explanation of the field’s purpose.
@i18n is an optional attribute holding the key to localization phrase of the form (see localization). |
| 5 | occurrences is an optional field used to control the number of values stored by a single input.
@minimum set to to zero means the input is not mandatory @maximum to zero means there is no upper limit to the number of values. This element is optional, if omitted the default will be minimum="0" and maximum="1". |
| 6 | config is an optional element designed to hold custom configuration for each input-type. |