Clustered deployments
Contents
This section describes how to create a clustered XP7 deployment.
Infrastructure requirements
Enonic XP clusters have basic infrastructure requirements, you will at least need:
-
Access to Compute units (VM’s or containers)
-
Local storage (Volumes)
-
A Distributed (or shared) filesystem
-
A Load balancer - to make sure traffic is routed to different nodes
These components are standard ingredients in most cloud services, or available as software components. An XP cluster can be launched using containers (including Kubernetes), traditional VMs, or even be running on your local computer.
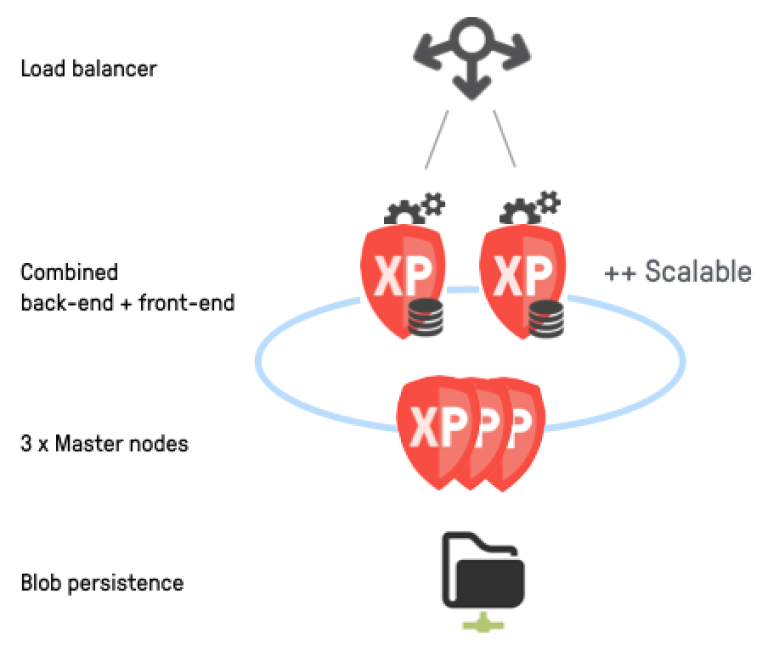
Basic cluster
In a cluster, each XP node can serve different purposes. In general, these are:
- Master node
-
Node that helps manage the cluster, and prevent split-brain scenarios
- Back-end node
-
Node that stores data, but does not handle incoming traffic
- Front-end node
-
Node that handles incoming traffic, but does not store data
- Combined node
-
Node that both stores data, and handles incoming traffic
Throughout this guide, we will describe how to setup a basic cluster, but with little more effort you could create any type of cluster. A basic cluster consists of 3 dedicated XP master nodes and 2 XP combined nodes.
For more examples on how to deploy XP, check out the various deployment strategies
Networking
| This guide assumes that you are deploying XP version 7.4 or higher |
To deploy a basic cluster, we need a total of 5 nodes for XP. You need to ensure that those servers can communicate on the following ports:
-
5701for hazelcast cluster communication -
9300for elasticsearch cluster communication
Storage
You will also need access to a shared file system for the servers. Read more about that in the Directories section. If you are using NFS as your shared file system you should also ensure that all XP nodes can communicate to the NFS server (typically on port 2049).
| Using NFS introduces a single point of failure to the cluster, but has generally proven highly reliable. |
CPU and memory
A combined node running XP should minimum have 4GB of memory and 2vCPU. A general recommendation would be 16GB memory and 4vCPU compute power.
Master nodes can be configured with less memory and capacity as they are generally not processing requests or queries.
Since Elasticsearch is embedded in XP, be sure also to setup virtual memory, file descriptors and swap setting correctly for elasticsearch. Read more about that in the elasticsearch documentation.
XP node setup
Setting up XP in a clustered configuration is pretty straight forward, but there are some things to consider.
Cluster config
There are 3 configuration files that enable cluster setup. Those are:
-
com.enonic.xp.cluster.cfg -
com.enonic.xp.elasticsearch.cfg -
com.enonic.xp.hazelcast.cfg
We will set the bare minimum for those files. You can read the Configuration documentation for more details.
| We assume that the IP addresses for the nodes are 10.0.0.1, 10.0.0.2, 10.0.0.3, 10.0.0.4 and 10.0.0.5. |
# Enable cluster and set node name
cluster.enabled=true
# This should be different for every node
node.name=master-1
# Bind to an IP and publish the same IP to other cluster members
# This should be different for every node
network.host=10.0.0.1
# This should be different for every node
network.publish.host=10.0.0.1
# Discover nodes on a comma separated list of node IPs
discovery.unicast.hosts=10.0.0.1,10.0.0.2,10.0.0.3,10.0.0.4,10.0.0.5# Set cluster name
cluster.name=demo_cluster
# Set node type
# This should only be true on the master nodes
node.master=true
# This should only be true on the data (combined) nodes
node.data=false
# Set minimum master nodes to ((number of master nodes) / 2) + 1
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes=2# Set minimum hazelcast cluster size to ((number of total nodes) / 2) + 1
system.hazelcast.initial.min.cluster.size=3Heap
Since XP is using elasticsearch for storage, we have to consider that elasticsearch uses off heap memory buffers. For that reason we cannot allocate all available memory to heap. In general you should:
-
Set heap memory to
75%of available memory on dedicated master nodes. -
Set heap memory to
30%of available memory on other nodes. -
Never allocate more than
26Gof heap.
You should set the heap memory with the XP_OPTS environmental variable. For example, if you want to give XP 512MB of heap you set XP_OPTS to -Xms512M -Xmx512M.
Options
You might want to pass options to the JVM. Our distributions set the JAVA_OPTS variable with defaults for XP to run smoothly. For that reason you should avoid overwriting JAVA_OPTS and instead you should use XP_OPTS to pass your options.
Directories
As mentioned above, you need a shared file system to run XP in a cluster. The directories that need to be shared are:
- $XP_HOME/repo/blob
-
Contains all files managed by XP.
- $XP_HOME/snapshots
-
Contains elasticsearch index snapshots.
- $XP_HOME/data
-
Contains other data (e.g. system dumps).
You need to mount those specific directories to the shared file system before you start XP.
You should never share $XP_HOME/repo/index and $XP_HOME/work between nodes. |
If you decide to change location of $XP_HOME/snapshots from default you must change values of both path.repo in com.enonic.xp.elasticsearch.cfg and snapshots.dir in com.enonic.xp.repo.cfg parameters. |
Pre-installed apps
You can pre-install apps in XP by placing the jars of those apps to $XP_HOME/deploy. We recommend placing the snapshotter app there to enable automatic snapshots.
| The pre-installed apps can be placed on distinct nodes, but for instance in the case of the snapshotter app, it should simply be placed on all nodes. |
Shard replication
Once your cluster has started you will have to set the number of shard replicas you want the data nodes to store. In this case we have 2 data nodes, so we want 2 copies of each shard in the cluster (1 per data node). To do that we should set the number of replicas to 1. Setting that number to 1 means that the cluster will have 1 primary shard, and 1 replica shard, totalling 2 copies. We can do this with the Enonic CLI:
$ export ENONIC_CLI_REMOTE_URL=10.0.0.1:4848
$ enonic repo replicas 1 --auth user:password
Setting replicas number to 1...Done
{
"UpdatedIndexes": [
"storage-system.auditlog",
"search-com.enonic.cms.default",
"storage-com.enonic.cms.default",
"search-system.auditlog",
"search-system-repo",
"storage-system-repo"
]
}Load balancing
When running XP in a cluster, we generally recommend using sticky sessions. Sticky sessions ensures requests from the same users is always passed to the same node in the cluster. This is due to the following reasons.
-
When performing write operations to the NoSQL data store, writing to one node, and then reading from another node immediately afterwards might not provide the result one expects - due to the distributed storage.
-
Any kind of node-local file handling will ONLY work across requests if the request is handled by the same node.
-
Performance is generally better and more consistent for users
For session-based logins, XP now supports session replication between nodes. This effectively prevents users from loosing their session, even when a node is stopped, but this does not mitigate the problems mentioned above.
Backup and restore
Like described in the Directories section, we have 3 directories that are shared between all the nodes. Of those three, you need to backup two:
-
$XP_HOME/repo/blob -
$XP_HOME/snapshots
With those 2 directories backed up, you can restore the files and indexes from your backups in case of a disaster.
For more details, check out the Backup and restore section.
Summary
Now you should have a good starting point to create clustered deployments. Just remember these bullet points:
-
Do not run nodes on the same physical hardware. That makes the clustered deployment more susceptible to failures.
-
Make sure ports
5701and9300is open between all cluster members. -
Setup virtual memory, file descriptors and swap setting on servers correctly.
-
Tailor the 3 cluster configuration files to your setup.
-
Set heap memory with the
-Xmsand-Xmxparameters using theXP_OPTSenvironmental variable. -
Avoid overwriting the
JAVA_OPTSenvironmental variable, useXP_OPTS. -
Take care of how much memory you allocate to heap. Set it to
30%of available RAM on all nodes, except if the node is a dedicated master node. Then you can set it to75%. -
Directories
$XP_HOME/repo/blob,$XP_HOME/snapshotsand$XP_HOME/datashould be shared between all nodes. -
The
$XP_HOME/repo/indexvolume should never be shared between nodes. -
Pre-install the snapshotter app for automatic snapshots.
-
Set the correct number of replicas after the cluster starts.
-
Backup
$XP_HOME/repo/bloband$XP_HOME/snapshots -
Use sticky sessions in your loadbalancer.
Q&A
What are the INFO c.h.i.diagnostics.HealthMonitor messages in the log file?
Enonic XP uses Hazelcast for clustering capabilities. Hazelcast HealthMonitor prints metrics logs when certain values (memory usage and system load) exceed 70% threshold. It is an indicator of server/cluster capacity problem, if such logs appear often. Occasional HealthMonitor log messages can be safely ignored.
My master nodes throw OutOfMemoryError even when they have 4GB of memory. What do I do?
Master nodes should be freed form heavy operations as they are on duty to keep cluster state healthy. Yet often great amount of work is put on them with inlined or named tasks run by applications. If heavy tasks must execute on master nodes (i.e. they have isMaster check), try to lower allocated heap from 75% to 50% of available RAM and allocate more total RAM for the master servers.
Starting from XP version 7.6.0 it is possible to free master nodes from running named tasks by setting distributable.acceptInbound = false in Task config.